Dental trauma
Trauma is the only real urgency in dentistry: in most cases, the amount of time that passes from the moment of trauma to the dentist’s intervention makes a difference to the prognosis of the teeth involved.
Emergencies❗
Is the dental practice closed? No problem!
Call our phone number and your call will be transferred.
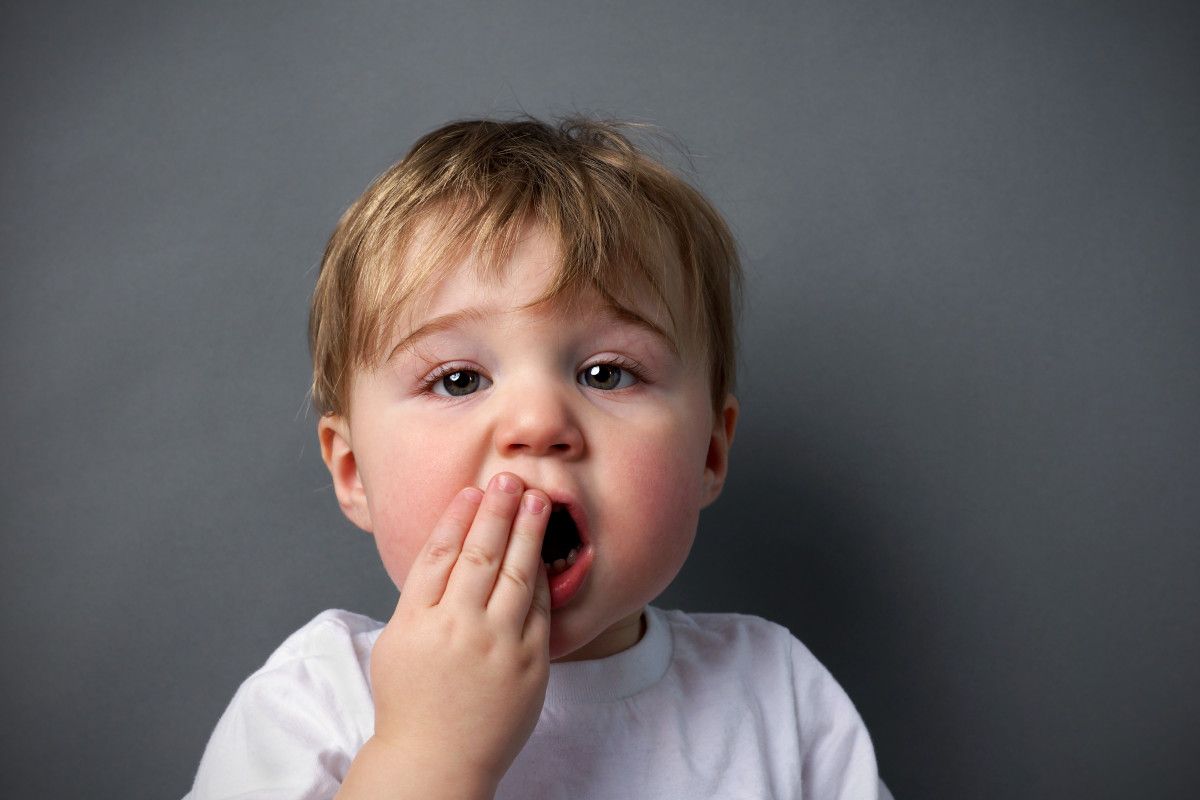

In case of trauma, it is important to contact the dentist as soon as possible. They are the only ones able to intervene promptly and in the correct way. Often, even the general emergency room proves useless due to the absence of suitable means, and there is a risk of losing valuable time.
Anyone who is not an expert is not able to assess the extent of the damage or the timing of the intervention: when a child bangs their teeth in front of you, it is important to contact us immediately.
What should you do
while waiting for the visit?
Primary Teeth Trauma
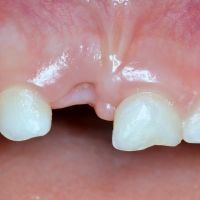
Even in the case of a fracture of the crown of a primary tooth, that is, when a piece of tooth breaks, it is good to have the child visit as soon as possible, but you can wait until the practice is open.
In the case of dislocation, when the tooth moves a lot and the gum is injured, a lot of blood can come out. It is recommended that the gum is swabbed with gauze or a handkerchief (although avoid using cotton wool), an ice pack is applied, and you call the practice as soon as possible.
If the practice is closed, use the emergency system only if the child cannot close their mouth or if the tooth moves a lot.
In case of loss of the primary tooth, you should not try to reposition it. The tooth should not be replanted so as not to risk problems with the underlying permanent tooth. However, it is important to look for it and take it to the practice: the dentist can then check if the tooth is fractured and check if there has been a total intrusion.
An avulsion (loss of the tooth) can, in fact, be a total intrusion in which the tooth has risen upwards until it disappears. Once in the practice, we can perform an X-ray that will prevent any doubts, but finding the missing tooth is already a helpful action.
It is recommended, in any case, that the gum is swabbed with gauze or a handkerchief (although avoid using cotton wool), an ice pack is applied, and you call the practice as soon as possible. If the practice is closed you can wait until it opens.
Trauma to permanent teeth
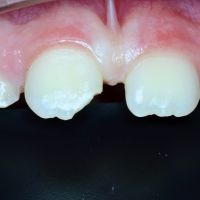
When the child gnashes their teeth, they often lose blood from the gum and, after a while, it can seem as if nothing has happened. It is still important to have a checkup because sometimes even mild trauma can cause damage to the tooth. You can wait until the practice is open.
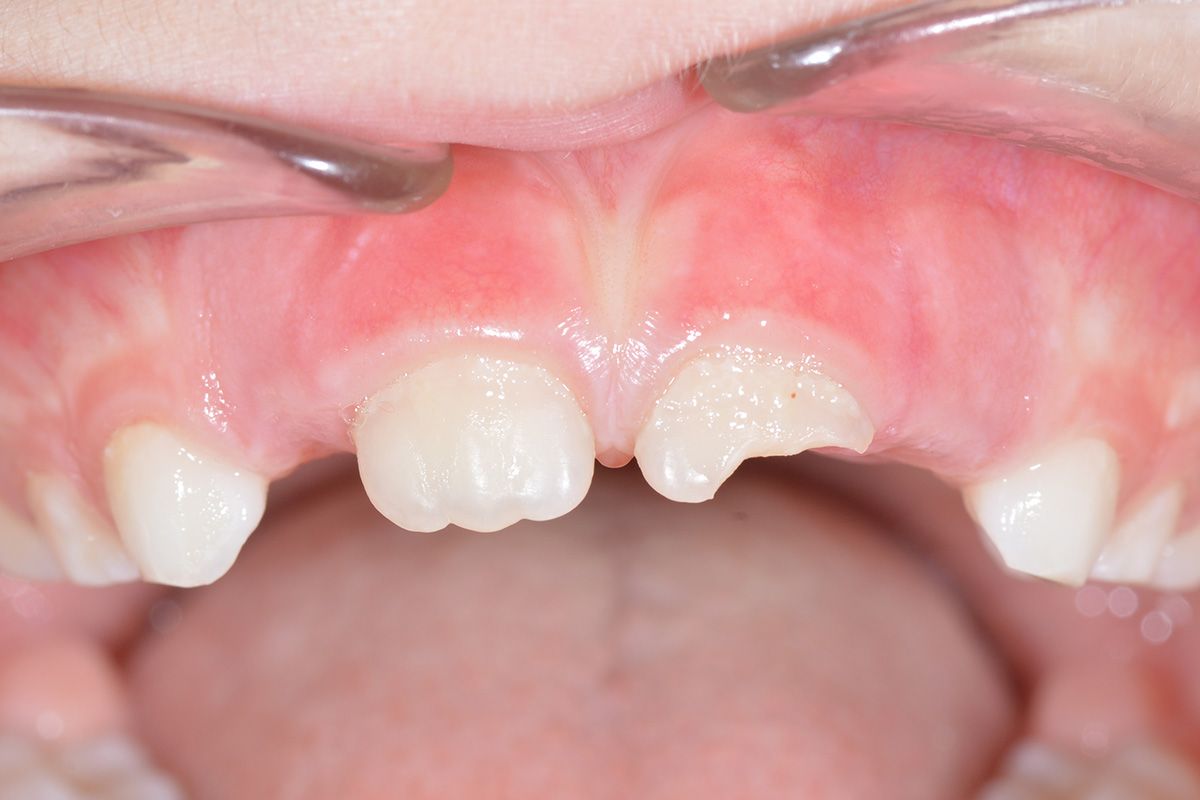
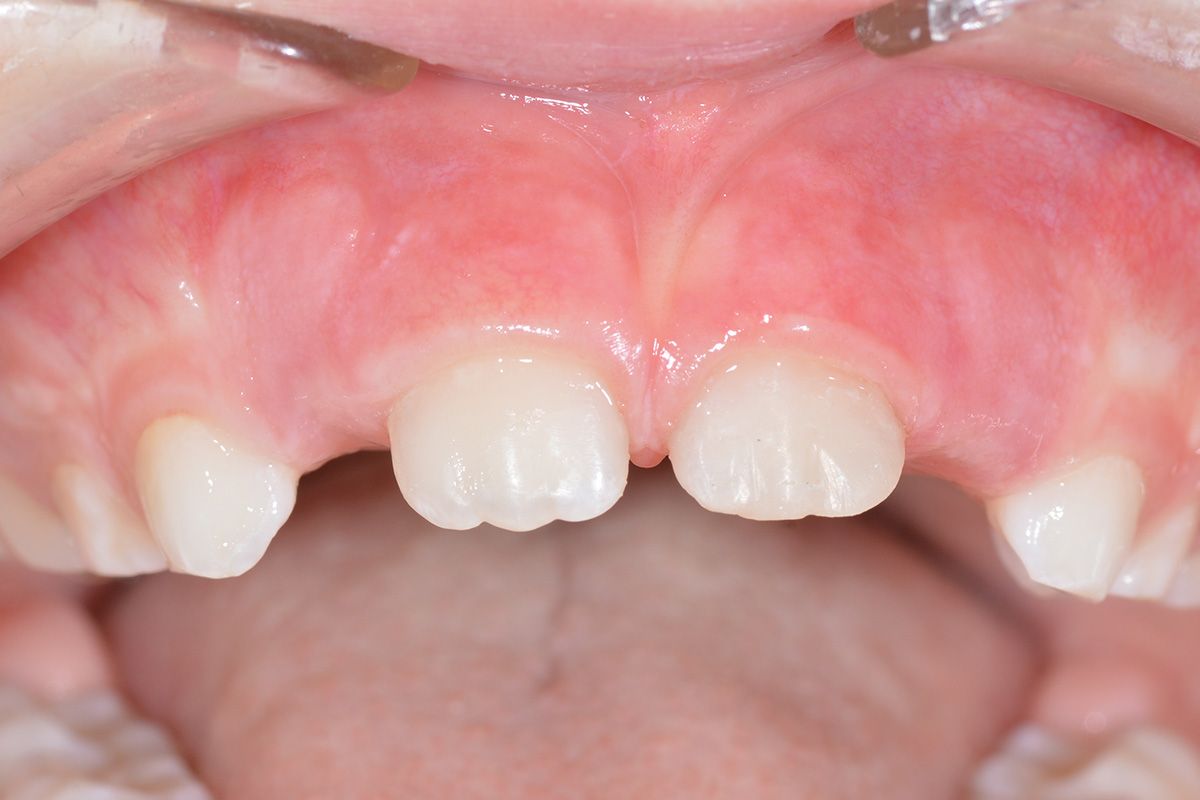
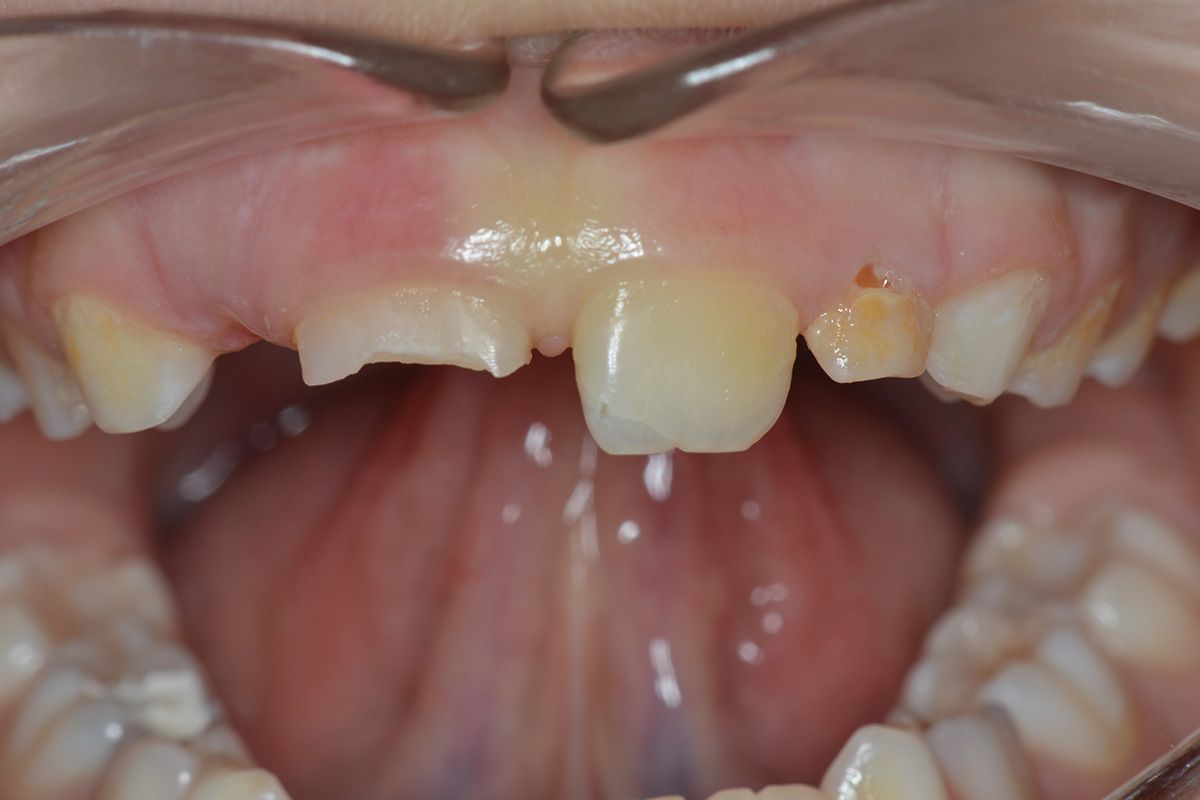
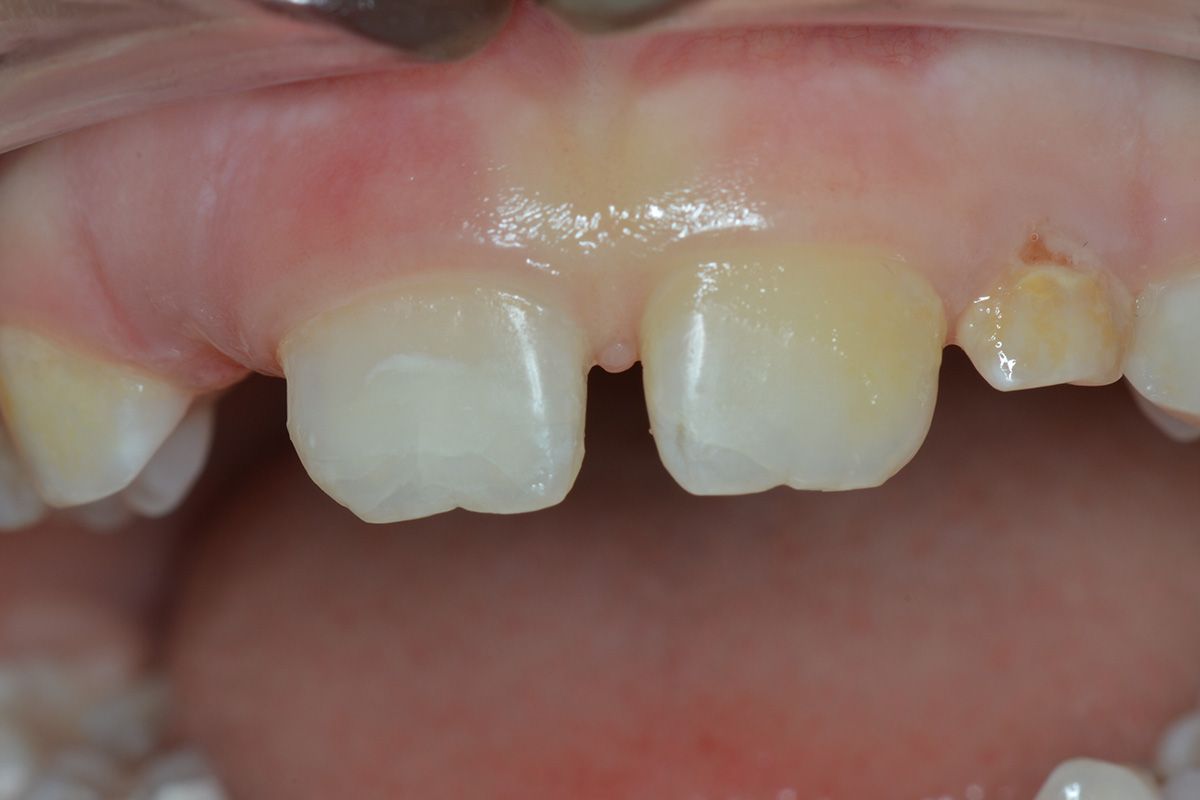
In case of a permanent tooth crown fracture, that is, when a piece of tooth breaks, it is important to look for the missing piece because it can be reattached. The tooth fragment must remain hydrated: it must be immersed in a liquid, preferably saline solution. In the case that you can’t find the fragment, don’t worry!
It will be possible to reconstruct the tooth using special materials. You should call the practice as soon as possible. If the practice is closed, use the emergency system.
If the tooth has moved, it wobbles, and blood comes out of the gum – dislocation – the element must be repositioned immediately. It is therefore necessary to call the practice as soon as possible or use the emergency system. In the meantime, use an ice pack and swab the gum with gauze or, in absence of this, a handkerchief.
In the case of total avulsion of the permanent tooth, when the permanent tooth comes out completely, it is essential to know what to do – the more time the tooth spends outside the socket, the more you risk not being able to recover it anymore.
We recommend calling the practice immediately. If the practice is closed, use the emergency system.
Meanwhile
- swab the gum and clean the area;
- look for the tooth and collect it, trying not to touch the root (i.e. taking it from the crown);
- if the tooth is dirty, rinse it, but do not disinfect it;
- if the parent can, they can try to put the tooth back in its place immediately but care must be taken to position it in the right direction, looking at the tooth next to it – you must still go to the practice as soon as possible because the tooth must be stabilised;
- if the parent does not do this, it is very important to keep the tooth hydrated by immersing it in a liquid, preferably saline solution, milk, or even water, or use the child’s saliva (by making the child spit into a container);
- try to get to the practice as quickly as possible, ideally in less than half an hour and within three hours at the most.